Thomas Telford on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thomas Telford FRS,
 At the age of 14, he was apprenticed to a stonemason, and some of his earliest work can still be seen on the bridge across the River Esk in
At the age of 14, he was apprenticed to a stonemason, and some of his earliest work can still be seen on the bridge across the River Esk in
 Among other structures, this involved the spectacular
Among other structures, this involved the spectacular  The same period also saw Telford involved in the design and construction of the
The same period also saw Telford involved in the design and construction of the
 During his later years, Telford was responsible for rebuilding sections of the London to Holyhead road, a task completed by his assistant of ten years, John MacNeill; today, much of the route is the A5 trunk road, although the Holyhead Road diverted off the A5 along what is now parts of A45, A41 and A464 through the cities of
During his later years, Telford was responsible for rebuilding sections of the London to Holyhead road, a task completed by his assistant of ten years, John MacNeill; today, much of the route is the A5 trunk road, although the Holyhead Road diverted off the A5 along what is now parts of A45, A41 and A464 through the cities of  Telford also worked on the North Wales coast road between Chester and Bangor, including another major suspension bridge at
Telford also worked on the North Wales coast road between Chester and Bangor, including another major suspension bridge at
 An Act of Parliament in 1823 provided a grant of £50,000 for the building of up to 40 churches and manses in communities without any church buildings (hence the alternative name: 'Parliamentary Church' or 'Parliamentary Kirk'). The total cost was not to exceed £1500 on any site and Telford was commissioned to undertake the design. He developed a simple church of T-shaped plan and two manse designs – a single-storey and a two-storey, adaptable to site and ground conditions, and to brick or stone construction, at £750 each. Of the 43 churches originally planned, 32 were eventually built around the Scottish highlands and islands (the other 11 were achieved by redoing existing buildings). The last of these churches was built in 1830. Some have been restored and/or converted to private use.
An Act of Parliament in 1823 provided a grant of £50,000 for the building of up to 40 churches and manses in communities without any church buildings (hence the alternative name: 'Parliamentary Church' or 'Parliamentary Kirk'). The total cost was not to exceed £1500 on any site and Telford was commissioned to undertake the design. He developed a simple church of T-shaped plan and two manse designs – a single-storey and a two-storey, adaptable to site and ground conditions, and to brick or stone construction, at £750 each. Of the 43 churches originally planned, 32 were eventually built around the Scottish highlands and islands (the other 11 were achieved by redoing existing buildings). The last of these churches was built in 1830. Some have been restored and/or converted to private use.
 In 2011 he was one of seven inaugural inductees to the
In 2011 he was one of seven inaugural inductees to the

 Telford designed a number of bridges and aqueducts during his career. They include:
Telford designed a number of bridges and aqueducts during his career. They include:
 Telford is commemorated through the naming of a number of sites:
*
Telford is commemorated through the naming of a number of sites:
*
The Life of Thomas Telford; civil engineer with an introductory history of roads and travelling in Great Britain
' Samuel Smiles (1867) *''Thomas Telford''
Menai Heritage
A community project and museum telling the story of Thomas Telford's Menai Suspension bridge
Revolutionary Players website
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Telford, Thomas 1757 births 1834 deaths British bridge engineers Scottish architects Scottish civil engineers Scottish philanthropists Scottish stonemasons Scottish autobiographers Fellows of the Royal Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences People from Dumfries and Galloway People of the Industrial Revolution Burials at Westminster Abbey British canal engineers Presidents of the Institution of Civil Engineers Harbour engineers Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame inductees
FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
, (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
, he designed numerous infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed ''The Colossus of Roads'' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewage ...
in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first President of the Institution of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters are located in the UK, whi ...
, a post he held for 14 years until his death.
The town of Telford
Telford () is a town in the borough of Telford and Wrekin and ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Shropshire, England, about east of Shrewsbury, south west of Stafford, north west of Wolverhampton and from Birmingham in t ...
in Shropshire was named after him.
Early career
Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, ahill farm
Hill farming or terrace farming is an extensive farming in upland areas, primarily rearing sheep, although historically cattle were often reared extensively in upland areas. Fell farming is the farming of fells, a fell being an area of unculti ...
east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or m ...
of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. Thomas was raised in poverty by his mother Janet Jackson (died 1794).
 At the age of 14, he was apprenticed to a stonemason, and some of his earliest work can still be seen on the bridge across the River Esk in
At the age of 14, he was apprenticed to a stonemason, and some of his earliest work can still be seen on the bridge across the River Esk in Langholm
Langholm , also known colloquially as the "Muckle Toon", is a burgh in Dumfries and Galloway, southern Scotland. Langholm lies between four hills in the valley of the River Esk in the Southern Uplands.
Location and geography
Langholm sits nort ...
in Dumfries and Galloway. He worked for a time in Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
and in 1782 he moved to London where, after meeting architects Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his ...
and Sir William Chambers, he was involved in building additions to Somerset House there. Two years later he found work at Portsmouth dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
and – although still largely self-taught – was extending his talents to the specification, design and management of building projects.
In 1787, through his wealthy patron William Pulteney, he became Surveyor of Public Works in Shropshire. His projects included renovation of Shrewsbury Castle
Shrewsbury Castle is a red sandstone castle in Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England. It stands on a hill in the neck of the meander of the River Severn on which the town originally developed. The castle, directly above Shrewsbury railway station, is ...
, the town's prison (during the planning of which he met leading prison reformer John Howard
John Winston Howard (born 26 July 1939) is an Australian former politician who served as the 25th prime minister of Australia from 1996 to 2007, holding office as leader of the Liberal Party. His eleven-year tenure as prime minister is the ...
), the Church of St. Mary Magdalene, Bridgnorth and another church, St Michael
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also ...
, in Madeley. Called in to advise on a leaking roof at St Chad's Church, Shrewsbury in 1788, he warned the church was in imminent danger of collapse; his reputation was made locally when it collapsed 3 days later, but he was not the architect for its replacement.
As the Shropshire county surveyor
A county surveyor is a public official in the United Kingdom and the United States.
United Kingdom
Webb & Webb describe the increasing chaos that began to prevail within this same period in field of county surveying in England and Wales, with c ...
, Telford was also responsible for bridges. In 1790 he designed a bridge carrying the London– Holyhead road over the River Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
at Montford, the first of some 40 bridges he built in Shropshire, including major crossings of the Severn at Buildwas
Buildwas is a village and civil parish in Shropshire, England, on the north bank of the River Severn at . It lies on the B4380 road between Atcham and Ironbridge. The Royal Mail postcodes begin TF6 and TF8.
Buildwas Primary Academy is situa ...
, and Bridgnorth
Bridgnorth is a town in Shropshire, England. The River Severn splits it into High Town and Low Town, the upper town on the right bank and the lower on the left bank of the River Severn. The population at the 2011 Census was 12,079.
Histor ...
. The bridge at Buildwas was Telford's first iron bridge. He was influenced by Abraham Darby's bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
at Ironbridge
Ironbridge is a large village in the borough of Telford and Wrekin in Shropshire, England. Located on the bank of the River Severn, at the heart of the Ironbridge Gorge, it lies in the civil parish of The Gorge. Ironbridge developed beside, a ...
, and observed that it was grossly over-designed for its function, and many of the component parts were poorly cast. By contrast, his bridge was wider in span and half the weight, although it now no longer exists. He was one of the first engineers to test his materials thoroughly before construction. As his engineering prowess grew, Telford was to return to this material repeatedly.
In 1795, the bridge at Bewdley
Bewdley ( pronunciation) is a town and civil parish in the Wyre Forest District in Worcestershire, England on the banks of the River Severn. It is in the Severn Valley west of Kidderminster and southwest of Birmingham. It lies on the Riv ...
in Worcestershire was swept away in the winter floods and Telford was responsible for the design of its replacement. The same winter floods saw the bridge at Tenbury
Tenbury Wells (locally Tenbury) is a market town and civil parish in the northwestern extremity of the Malvern Hills District of Worcestershire, England. Its northern border adjoins Shropshire, and at the 2011 census it had a population of 3,777. ...
also swept away. This bridge across the River Teme
The River Teme (pronounced ; cy, Afon Tefeidiad) rises in Mid Wales, south of Newtown, and flows southeast roughly forming the border between England and Wales for several miles through Knighton before entering England in the vicinity of B ...
was the joint responsibility of both Worcestershire and Shropshire and the bridge has a bend where the two counties meet. Telford was responsible for the repair to the northern (Shropshire) end of the bridge.
Ellesmere Canal
Telford's reputation in Shropshire led to his appointment in 1793 to manage the detailed design and construction of the Ellesmere Canal, linking the ironworks and collieries ofWrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
via the north-west Shropshire town of Ellesmere, with Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
, utilising the existing Chester Canal
The Chester Canal was an English canal linking the south Cheshire town of Nantwich with the River Dee at Chester. It was intended to link Chester to Middlewich, with a branch to Nantwich, but the Trent and Mersey Canal were unco-operative abou ...
, and then the River Mersey
The River Mersey () is in North West England. Its name derives from Old English and means "boundary river", possibly referring to its having been a border between the ancient kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria. For centuries it has formed part ...
.
 Among other structures, this involved the spectacular
Among other structures, this involved the spectacular Pontcysyllte Aqueduct
The Pontcysyllte Aqueduct (; cy, Traphont Ddŵr Pontcysyllte) is a navigable aqueduct that carries the Llangollen Canal across the River Dee in the Vale of Llangollen in northeast Wales.
The 18-arched stone and cast iron structure is for use ...
over the River Dee in the Vale of Llangollen
Llangollen () is a town and community, situated on the River Dee, in Denbighshire, Wales. Its riverside location forms the edge of the Berwyn range, and the Dee Valley section of the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Bea ...
, where Telford used a new method of construction consisting of troughs made from cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impuriti ...
plates and fixed in masonry. Extending for over with an altitude of above the valley floor, the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct consists of nineteen arches, each with a span. Being a pioneer in the use of cast-iron for large scaled structures, Telford had to invent new techniques, such as using boiling sugar and lead as a sealant on the iron connections.
Eminent canal engineer William Jessop
William Jessop (23 January 1745 – 18 November 1814) was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Early life
Jessop was born in Devonport, Devon, the ...
oversaw the project, but he left the detailed execution of the project in Telford's hands. The aqueduct was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2009.
 The same period also saw Telford involved in the design and construction of the
The same period also saw Telford involved in the design and construction of the Shrewsbury Canal
The Shrewsbury Canal (or Shrewsbury and Newport Canal) was a canal in Shropshire, England. Authorised in 1793, the main line from Trench to Shrewsbury was fully open by 1797, but it remained isolated from the rest of the canal network until 183 ...
. When the original engineer, Josiah Clowes, died in 1795, Telford succeeded him. One of Telford's achievements on this project was the design of Longdon-on-Tern Aqueduct
The Longdon-on-Tern Aqueduct, near Longdon-on-Tern in Shropshire, was one of the first two canal aqueducts to be built from cast iron.
History
The cast iron canal aqueduct was re-engineered by Thomas Telford after the first construction desig ...
, the cast-iron aqueduct at Longdon-on-Tern
Longdon-Upon-Tern (also known as Longdon-on-Tern or colloquially Longdon) is a village in east central Shropshire, England. It is in the unitary district of Telford and Wrekin, and is approximately east of Shrewsbury and north-west of Telfor ...
, pre-dating that at Pontcysyllte, and substantially bigger than the UK's first cast-iron aqueduct, built by Benjamin Outram
Benjamin Outram (1 April 1764 – 22 May 1805) was an English civil engineer, surveyor and industrialist. He was a pioneer in the building of canals and tramways.
Life
Born at Alfreton in Derbyshire, he began his career assisting his father ...
on the Derby Canal
The Derby Canal ran from the Trent and Mersey Canal at Swarkestone to Derby and Little Eaton, and to the Erewash Canal at Sandiacre, in Derbyshire, England. The canal was authorised by an Act of Parliament in 1793 and was fully completed in 179 ...
just months earlier. The aqueduct is no longer in use, but is preserved as a distinctive piece of canal engineering.
The Ellesmere Canal was left uncompleted in 1805 because it failed to generate the revenues needed to finance the connecting sections to Chester and Shrewbury. However, alongside his canal responsibilities, Telford's reputation as a civil engineer meant he was constantly consulted on numerous other projects. These included water supply works for Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, improvements to London's docklands and the rebuilding of London Bridge (c. 1800).
Most notably (and again William Pulteney was influential), in 1801 Telford devised a master plan to improve communications in the Highlands of Scotland
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sco ...
, a massive project that was to last some 20 years. It included the building of the Caledonian Canal along the Great Glen
The Great Glen ( gd, An Gleann Mòr ), also known as Glen Albyn (from the Gaelic "Glen of Scotland" ) or Glen More (from the Gaelic ), is a glen in Scotland running for from Inverness on the edge of Moray Firth, in an approximately straight ...
and redesign of sections of the Crinan Canal, some of new roads, over a thousand new bridges (including the Craigellachie Bridge
Craigellachie Bridge is a cast iron arch bridge across the River Spey at Craigellachie, near to the village of Aberlour in Moray, Scotland. It was designed by the renowned civil engineer Thomas Telford and built from 1812 to 1814. It is a Catego ...
), numerous harbour improvements (including works at Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
, Dundee, Peterhead
Peterhead (; gd, Ceann Phàdraig, sco, Peterheid ) is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is Aberdeenshire's biggest settlement (the city of Aberdeen itself not being a part of the district), with a population of 18,537 at the 2011 Census. ...
, Wick
Wick most often refers to:
* Capillary action ("wicking")
** Candle wick, the cord used in a candle or oil lamp
** Solder wick, a copper-braided wire used to desolder electronic contacts
Wick or WICK may also refer to:
Places and placename ...
, Portmahomack
Portmahomack ( gd, Port Mo Chalmaig; 'Haven of My .e. 'Saint'Colmóc') is a small fishing village in Easter Ross, Scotland. It is situated in the Tarbat Peninsula in the parish of Tarbat. Tarbat Ness Lighthouse is about from the village at ...
and Banff), and 32 new churches.
Telford also undertook highway works in the Scottish Lowlands, including of new roads and numerous bridges, ranging from a 112 ft (34 m) span stone bridge across the Dee at Tongueland in Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbright ( ; sco, Kirkcoubrie; gd, Cille Chùithbeirt) is a town, parish and a Royal Burgh from 1455 in Kirkcudbrightshire, of which it is traditionally the county town, within Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.
The town lies southwest of ...
(1805–06) to the 129 ft (39 m) tall Cartland Crags bridge near Lanark
Lanark (; gd, Lannraig ; sco, Lanrik) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, located 20 kilometres to the south-east of Hamilton. The town lies on the River Clyde, at its confluence with Mouse Water. In 2016, the town had a population of 9 ...
(1822).
In 1809, Telford was tasked with improving the Howth Road
Howth ( ; ; non, Hǫfuð) is an affluent peninsular village and outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland. The district as a whole occupies the greater part of the peninsula of Howth Head, which forms the northern boundary of Dublin Bay, and includes ...
in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
, to connect the new harbour at Howth
Howth ( ; ; non, Hǫfuð) is an affluent peninsular village and outer suburb of Dublin, Ireland. The district as a whole occupies the greater part of the peninsula of Howth Head, which forms the northern boundary of Dublin Bay, and includes ...
to the city of Dublin as part of wider plan to improve communication between Dublin and London. The milestones that are a feature of this route from Howth to the GPO GPO may refer to:
Government and politics
* General Post Office, Dublin
* General Post Office, in Britain
* Social Security Government Pension Offset, a provision reducing benefits
* Government Pharmaceutical Organization, a Thai state enterpris ...
on O'Connell Street
O'Connell Street () is a street in the centre of Dublin, Ireland, running north from the River Liffey. It connects the O'Connell Bridge to the south with Parnell Street to the north and is roughly split into two sections bisected by Henry S ...
still mark the route. He also drafted the first design of the Ulster Canal
The Ulster Canal is a canal running through part of County Armagh, County Tyrone and County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland and County Monaghan in the Republic of Ireland. The Ulster Canal was built between 1825 and 1842 and was 74 km (46&nb ...
. Irish engineer, William Dargan
William Dargan (28 February 1799 – 7 February 1867) was arguably the most important Irish engineer of the 19th century and certainly the most important figure in railway construction. Dargan designed and built Ireland's first railway lin ...
, was trained by Telford.
Telford was consulted in 1806 by the King of Sweden
The monarchy of Sweden is the monarchical head of state of Sweden,See the Instrument of Government, Chapter 1, Article 5. which is a constitutional and hereditary monarchy with a parliamentary system.Parliamentary system: see the Instrument o ...
about the construction of a canal between Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has ...
and Stockholm
Stockholm () is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, largest city of Sweden as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people liv ...
. His plans were adopted and construction of the Göta Canal
The Göta Canal ( sv, Göta kanal) is a Swedish canal constructed in the early 19th century.
The canal is long, of which were dug or blasted, with a width varying between and a maximum depth of about .Uno Svedin, Britt Hägerhäll Anianss ...
began in 1810. Telford travelled to Sweden at that time to oversee some of the more important initial excavations.
Many of Telford's projects were undertaken due to his role as a member of the Exchequer Bill Loan Commission
The Exchequer Bill Loan Commission of the United Kingdom was set up under the Poor Employment Act, Poor Employment Act 1817, to help finance public work projects that would generate employment. Commissioners included Thomas Telford and Francis Ludl ...
, an organ set up under the Poor Employment Act
The Poor Employment Act 1817 (officially the Public Works Loans Act 1817), 57 Geo III was an act passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
The act was passed in order ''"to authorise the issue of Exchequer Bills and the Advance of Money out ...
of 1817, to help finance public work projects that would generate employment.
The 'Colossus of Roads'
 During his later years, Telford was responsible for rebuilding sections of the London to Holyhead road, a task completed by his assistant of ten years, John MacNeill; today, much of the route is the A5 trunk road, although the Holyhead Road diverted off the A5 along what is now parts of A45, A41 and A464 through the cities of
During his later years, Telford was responsible for rebuilding sections of the London to Holyhead road, a task completed by his assistant of ten years, John MacNeill; today, much of the route is the A5 trunk road, although the Holyhead Road diverted off the A5 along what is now parts of A45, A41 and A464 through the cities of Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its ...
, Birmingham and Wolverhampton
Wolverhampton () is a city, metropolitan borough and administrative centre in the West Midlands, England. The population size has increased by 5.7%, from around 249,500 in 2011 to 263,700 in 2021. People from the city are called "Wulfrunian ...
. Between London and Shrewsbury, most of the work amounted to improvements. Beyond Shrewsbury, and especially beyond Llangollen, the work often involved building a highway from scratch. Notable features of this section of the route include the
Waterloo Bridge
Waterloo Bridge () is a road and foot traffic bridge crossing the River Thames in London, between Blackfriars Bridge and Hungerford Bridge and Golden Jubilee Bridges. Its name commemorates the victory of the British, Dutch and Prussians at t ...
across the River Conwy
, name_etymology =
, image = Boats in River Conwy.jpg
, image_size = 300
, image_caption = Boats in the river estuary at Conwy
, map =
, map_size =
, map_caption =
, push ...
at Betws-y-Coed
Betws-y-coed (; '' en, prayer house in the wood'') is a village and community in the Conwy valley in Conwy County Borough, Wales, located in the historic county of Caernarfonshire, right on the boundary with Denbighshire, in the Gwydir Forest. ...
, the ascent from there to Capel Curig
Capel Curig (; meaning " Curig's Chapel") is a village and community in Conwy County Borough, Wales. Historically in Caernarfonshire, it lies in the heart of Snowdonia, on the River Llugwy, and has a population of 226, reducing slightly to 206 ...
and then the descent from the pass of Nant Ffrancon
The Nant Ffrancon Pass in Snowdonia, North Wales, is the long steady climb of the A5 road between Bethesda, Gwynedd, and Llyn Ogwen in Conwy. The summit at is at Pont Wern-gof, about one-third of a mile beyond the eastern end of Llyn Ogwen. Fr ...
towards Bangor. Between Capel Curig
Capel Curig (; meaning " Curig's Chapel") is a village and community in Conwy County Borough, Wales. Historically in Caernarfonshire, it lies in the heart of Snowdonia, on the River Llugwy, and has a population of 226, reducing slightly to 206 ...
and Bethesda, in the Ogwen Valley
Dyffryn Ogwen, or Ogwen Valley, is a valley mostly located in the Welsh county of Gwynedd. The upper section of the valley, east of Llyn Ogwen, lies in the county of Conwy.
Geography
The valley lies to the south of Bangor. It is bordered on ...
, Telford deviated from the original road, built by Romans during their occupation of this area.
On the island of Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
a new embankment
Embankment may refer to:
Geology and geography
* A levee, an artificial bank raised above the immediately surrounding land to redirect or prevent flooding by a river, lake or sea
* Embankment (earthworks), a raised bank to carry a road, railwa ...
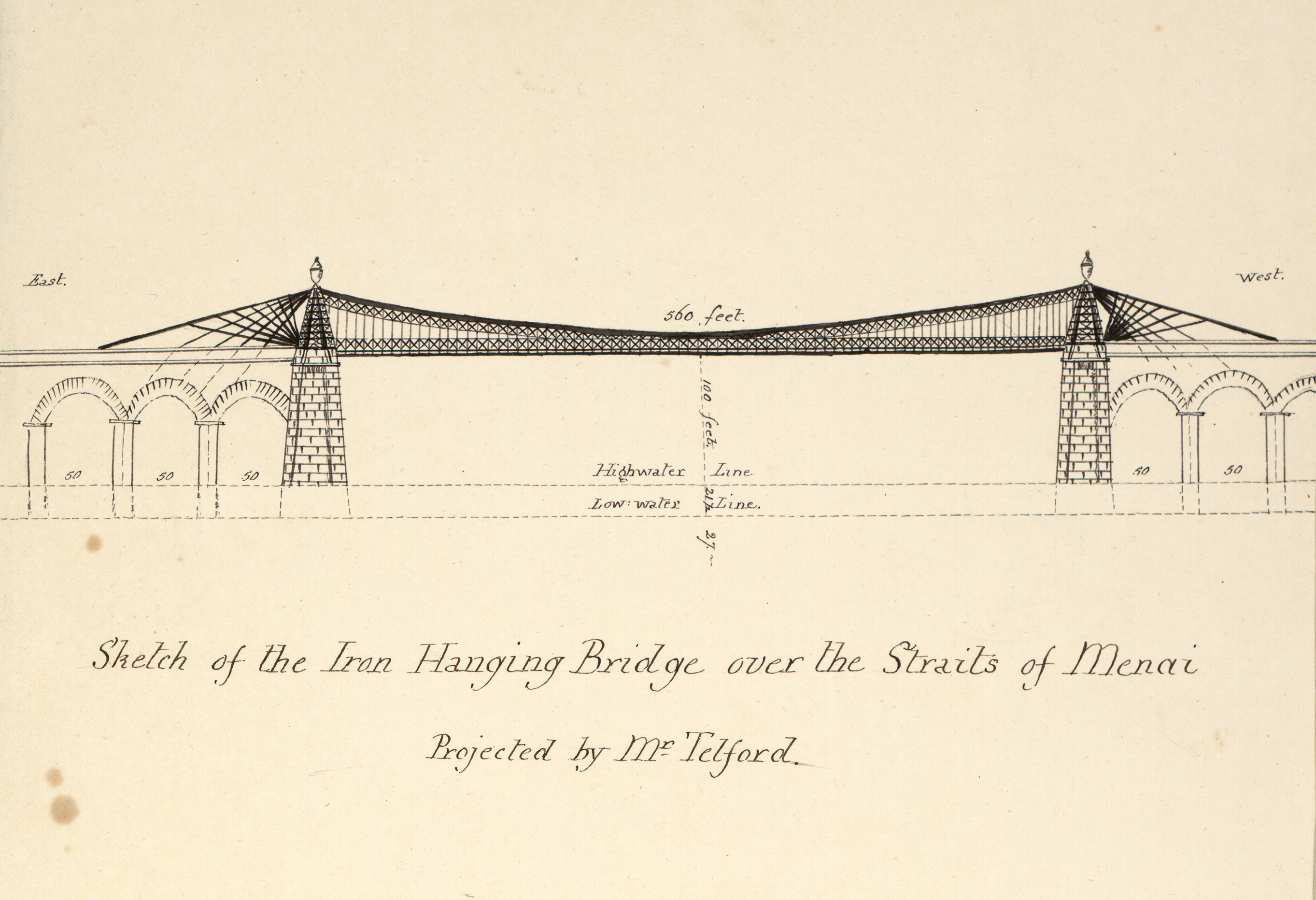
across the Stanley Sands to Holyhead was constructed, but the crossing of the Menai Strait was the most formidable challenge, overcome by the Menai Suspension Bridge
The Menai Suspension Bridge ( cy, Pont y Borth, Pont Grog y Borth) is a suspension bridge spanning the Menai Strait between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales. Designed by Thomas Telford and completed in 1826, it was the world's f ...
(1819–26). Spanning , this was the longest suspension bridge of the time. Unlike modern suspension bridges, Telford used individually linked iron eye bars for the cables.
Conwy
Conwy (, ), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town, community and the administrative centre of Conwy County Borough in North Wales. The walled town and castle stand on the west bank of the River Conwy, facing Deganwy on ...
, opened later the same year as its Menai counterpart.
Further afield Telford designed a road to cross the centre of the Isle of Arran. Named the 'String road', this route traverses bleak and difficult terrain to allow traffic to cross between east and west Arran avoiding the circuitous coastal route. His work on improving the Glasgow – Carlisle road, later to become the A74, has been described as "a model for future engineers."
Telford improved on methods for the building of macadam roads by improving the selection of stone based on thickness, taking into account traffic, alignment and slopes.
The punning nickname ''Colossus of Roads'' was given to Telford by his friend, the eventual Poet Laureate
A poet laureate (plural: poets laureate) is a poet officially appointed by a government or conferring institution, typically expected to compose poems for special events and occasions. Albertino Mussato of Padua and Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch ...
, Robert Southey
Robert Southey ( or ; 12 August 1774 – 21 March 1843) was an English poet of the Romantic school, and Poet Laureate from 1813 until his death. Like the other Lake Poets, William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Southey began as a ra ...
.
In 1821, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
The 'Telford Church'
 An Act of Parliament in 1823 provided a grant of £50,000 for the building of up to 40 churches and manses in communities without any church buildings (hence the alternative name: 'Parliamentary Church' or 'Parliamentary Kirk'). The total cost was not to exceed £1500 on any site and Telford was commissioned to undertake the design. He developed a simple church of T-shaped plan and two manse designs – a single-storey and a two-storey, adaptable to site and ground conditions, and to brick or stone construction, at £750 each. Of the 43 churches originally planned, 32 were eventually built around the Scottish highlands and islands (the other 11 were achieved by redoing existing buildings). The last of these churches was built in 1830. Some have been restored and/or converted to private use.
An Act of Parliament in 1823 provided a grant of £50,000 for the building of up to 40 churches and manses in communities without any church buildings (hence the alternative name: 'Parliamentary Church' or 'Parliamentary Kirk'). The total cost was not to exceed £1500 on any site and Telford was commissioned to undertake the design. He developed a simple church of T-shaped plan and two manse designs – a single-storey and a two-storey, adaptable to site and ground conditions, and to brick or stone construction, at £750 each. Of the 43 churches originally planned, 32 were eventually built around the Scottish highlands and islands (the other 11 were achieved by redoing existing buildings). The last of these churches was built in 1830. Some have been restored and/or converted to private use.
Late career
Other works by Telford include theSt Katharine Docks
St Katharine Docks is a former dock and now a mixed-used district in Central London, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets and within the East End. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, immediately downstream of the Tower of London an ...
(1824–28) close to Tower Bridge
Tower Bridge is a Listed building#Grade I, Grade I listed combined Bascule bridge, bascule and Suspended-deck suspension bridge, suspension bridge in London, built between 1886 and 1894, designed by Horace Jones (architect), Horace Jones and e ...
in central London, where he worked with the architect Philip Hardwick
Philip Hardwick (15 June 1792 in London – 28 December 1870) was an English architect, particularly associated with railway stations and warehouses in London and elsewhere. Hardwick is probably best known for London's demolished Euston Arch ...
, the Gloucester and Berkeley Ship Canal (today known as the Gloucester and Sharpness Canal
The Gloucester and Sharpness Canal (also known as the Gloucester and Berkeley Canal) is a ship canal in the west of England, between Gloucester and Sharpness; for much of its length it runs close to the tidal River Severn, but cuts off a sign ...
), Over Bridge
Over may refer to:
Places
*Over, Cambridgeshire, England
*Over, Cheshire, England
* Over, South Gloucestershire, England
*Over, Tewkesbury, near Gloucester, England
** Over Bridge
* Over, Seevetal, Germany
Music
Albums
* ''Over'' (album), by P ...
near Gloucester, the second Harecastle Tunnel
Harecastle Tunnel is a canal tunnel on the Trent and Mersey Canal in Staffordshire between Kidsgrove and Tunstall. The tunnel, which is long, was once one of the longest in the country. Its industrial purpose was for the transport of coal ...
on the Trent and Mersey Canal (1827), and the Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal
The Birmingham and Liverpool Junction Canal was a canal in England which ran from Nantwich, where it joined the Chester Canal, to Autherley, where it joined the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal. Forming part of a major link between Liverp ...
(today part of the Shropshire Union Canal) – started in May 1826 but finished, after Telford's death, in January 1835. At the time of its construction in 1829, Galton Bridge
The Galton Bridge is a cast-iron bridge in Smethwick, near Birmingham, in central England. Opened in 1829 as a road bridge, the structure has been pedestrianised since the 1970s. It was built by Thomas Telford to carry a road across the new mai ...
was the longest single span in the world. Telford surveyed and planned the Macclesfield Canal, which was completed by William Crosley (or Crossley). He also built Whitstable
Whitstable () is a town on the north coast of Kent adjoining the convergence of the Swale Estuary and the Greater Thames Estuary in southeastern England, north of Canterbury and west of Herne Bay. The 2011 Census reported a population of ...
harbour in Kent in 1832, in connection with the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway
The Canterbury and Whitstable Railway, sometimes referred to colloquially as the "Crab and Winkle Line", was an early British railway that opened in 1830 between Canterbury and Whitstable in the county of Kent, England.
Early history
Ther ...
with an unusual system for flushing out mud using a tidal reservoir. He also completed the '' Grand Trunk'' after James Brindley
James Brindley (1716 – 27 September 1772) was an English engineer. He was born in Tunstead, Derbyshire, and lived much of his life in Leek, Staffordshire, becoming one of the most notable engineers of the 18th century.
Early life
Born i ...
died due to being over-worked.
In 1820, Telford was appointed the first President of the recently formed Institution of Civil Engineers
The Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) is an independent professional association for civil engineers and a charitable body in the United Kingdom. Based in London, ICE has over 92,000 members, of whom three-quarters are located in the UK, whi ...
, a post he held until his death.
Freemasonry
He was Initiated into Freemasonry in Antiquity Lodge, No. 26, (Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
, England) in 1770. This lodge no longer exists. He was a founder member of Phoenix Lodge, No. 257 (also in Portsmouth). Telford designed a room within the George Inn for the lodge. In 1786 he became an affiliate member of Salopian Lodge, No. 262 (Shrewsbury, England).
Telford's death
Telford's young draughtsman and clerk 1830–34 George Turnbull in his diary states:''On the 23rd'' ugust 1834''Mr Telford was taken seriously ill of a bilious derangement to which he had been liable … he grew worse and worse'' … urgeons''attended him twice a day, but it was to no avail for he died on the 2nd September, very peacefully at about 5pm. … His old servant James Handscombe and I were the only two in the house'' 4 Abingdon Street, London''when he died. He was never married. Mr Milne and MrThomas Telford was buried in the nave of Westminster Abbey; a statue was erected to him nearby, in St Andrew's Chapel adjoining the north transept. Throughout his life Telford had a great affection for his birthplace of Eskdale and its people and in his will left legacies to the two local libraries at Westerkirk and Langholm.Rickman Rickman is both a surname and a given name. As a surname, one origin is as the English version of the German surname Ryckman. Notable people with the name include: People with the surname Rickman: *Alan Rickman (1946–2016), English film, televi ...were, no doubt, Telford's most intimate friends. … I went to Mr Milne and under his direction … made all the arrangements about the house and correspondence. … Telford had no blood relations that we knew of. The funeral took place on the 10th September n_Westminster_Abbey.html" ;"title="Westminster_Abbey.html" ;"title="n Westminster Abbey">n Westminster Abbey">Westminster_Abbey.html" ;"title="n Westminster Abbey">n Westminster Abbey … Mr Telford was of the most genial disposition and a delightful companion, his laugh was the heartiest I ever heard; it was a pleasure to be in his society.''Diaries of George Turnbull (Chief Engineer, East Indian Railway Company) held at the Centre of South Asian Studies at Cambridge University, England
Honours
 In 2011 he was one of seven inaugural inductees to the
In 2011 he was one of seven inaugural inductees to the Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame
The Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame honours "those engineers from, or closely associated with, Scotland who have achieved, or deserve to achieve, greatness", as selected by an independent panel representing Scottish engineering institutions, aca ...
.
Telford the poet
Telford's reputation as a man of letters may have preceded his fame as an engineer: he had published poetry between 1779 and 1784, and an account of a tour of Scotland with Robert Southey. His will left bequests to Southey (who would later write Telford's biography), the poet Thomas Campbell (1777–1844) and to the publishers of the ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia
The ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia'' is an encyclopaedia in 18 volumes, printed and published by William Blackwood and edited by David Brewster between 1808 and 1830. In competition with the Edinburgh-published ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', the ''Edin ...
'' (to which he had been a contributor).
George Turnbull states that Telford wrote and gave him a poem:
(Turnbull includes notes that explain nine references to Burns's life in the poem.)
Turnbull also states:
His ability and perseverance may be understood from various literary compositions of after life, such as the articles he contributed to the ''Another example, later in Telford's life, was ''To SirEdinburgh Encyclopædia The ''Edinburgh Encyclopædia'' is an encyclopaedia in 18 volumes, printed and published by William Blackwood and edited by David Brewster between 1808 and 1830. In competition with the Edinburgh-published ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', the ''Edin ...'', such as Architecture, Bridge-building, and Canal-making. Singular to say the earliest distinction he acquired in life was as a poet. Even at 30 years of age he reprinted at Shrewsbury a poem called "Eskdale", … Some others of his poems are in my possession.
John Malcolm
Major-General Sir John Malcolm GCB, KLS (2 May 1769 – 30 May 1833) was a Scottish soldier, diplomat, East India Company administrator, statesman, and historian.
Early life
Sir John Malcolm was born in 1769, one of seventeen children of Ge ...
on Receiving His Miscellaneous Poems'' (1831).
Bridges designed by Telford
 Telford designed a number of bridges and aqueducts during his career. They include:
Telford designed a number of bridges and aqueducts during his career. They include:
Places named after Telford
 Telford is commemorated through the naming of a number of sites:
*
Telford is commemorated through the naming of a number of sites:
* Telford
Telford () is a town in the borough of Telford and Wrekin and ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Shropshire, England, about east of Shrewsbury, south west of Stafford, north west of Wolverhampton and from Birmingham in t ...
New Town;
* Thomas Telford School
Thomas Telford School (commonly referred to as TTS) is a City Technology College in Telford, Shropshire and is sponsored by The Mercers Company and Tarmac Holdings Limited. Prior to 2016 the mixed ability school ranked as the top performing co ...
;
* Thomas Telford Road, Langholm, where Telford was an apprentice in his early years;
* Telford Hall, a hall of residence at Loughborough University. A plaque in his honour hangs in the hall's common room;
* Telford, Pennsylvania, the Borough of County Line in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania
Montgomery County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is the third-most populous county in Pennsylvania and the 73rd-most populous county in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the county was 856,55 ...
changed its name to Telford
Telford () is a town in the borough of Telford and Wrekin and ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Shropshire, England, about east of Shrewsbury, south west of Stafford, north west of Wolverhampton and from Birmingham in t ...
in 1857, after the North Pennsylvania Railroad
The North Pennsylvania Railroad was a railroad company which served Philadelphia, Montgomery County, Bucks County and Northampton County in Pennsylvania. It was formed in 1852 and began operation in 1855. The Philadelphia and Reading Railway, ...
Company named its new station there "Telford" in honour of Thomas Telford;
* Telford College, Edinburgh;
* Telford Bridge (footbridge), in 2008, a footbridge was erected over the Shubenacadie Canal
The Shubenacadie Canal is a canal in central Nova Scotia, Canada. It links Halifax Harbour with the Bay of Fundy by way of the Shubenacadie River and Shubenacadie Grand Lake. Begun in 1826, it was not completed until 1861 and was closed in 1871. ...
in Dartmouth, Nova Scotia
Dartmouth ( ) is an urban community and former city located in the Halifax Regional Municipality of Nova Scotia, Canada. Dartmouth is located on the eastern shore of Halifax Harbour. Dartmouth has been nicknamed the City of Lakes, after the larg ...
and named for Telford, who made important contributions to the nineteenth-century Canadian canal;
* Thomas Telford Basin, part of a residential development on the Ashton Canal
The Ashton Canal is a canal in Greater Manchester, England, linking Manchester with Ashton-under-Lyne.
Route
The Ashton leaves the Rochdale Canal at Ducie St. Junction in central Manchester, and climbs for through 18 locks, passing thro ...
in Manchester.
Autobiography
Telford's autobiography, titled ''The Life of Thomas Telford, Civil Engineer, written by himself'', was published posthumously in 1838.Bibliography
*The Life of Thomas Telford; civil engineer with an introductory history of roads and travelling in Great Britain
' Samuel Smiles (1867) *''Thomas Telford''
L. T. C. Rolt
Lionel Thomas Caswall Rolt (usually abbreviated to Tom Rolt or L. T. C. Rolt) (11 February 1910 – 9 May 1974) was a prolific English writer and the biographer of major civil engineering figures including Isambard Kingdom Brunel and Thomas Te ...
, Longmans (1958)
*''Thomas Telford'', Penguin (1979),
*''Thomas Telford, Engineer'', Thomas Telford Ltd (1980),
*''Man of Iron: Thomas Telford and the Building of Britain,'' Julian Glover
Julian Wyatt Glover (born 27 March 1935) is an English classical actor with many stage, television, and film roles since commencing his career in the 1950s. He is a recipient of the Laurence Olivier Award and has performed many times for the ...
, Bloomsbury Publishing (2017),
See also
*Works of Thomas Telford
Works may refer to:
People
* Caddy Works (1896–1982), American college sports coach
* Samuel Works (c. 1781–1868), New York politician
Albums
* '' ''Works'' (Pink Floyd album)'', a Pink Floyd album from 1983
* ''Works'', a Gary Burton album ...
*Telford Medal
The Telford Medal is a prize awarded by the British Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) for a paper or series of papers. It was introduced in 1835 following a bequest made by Thomas Telford, the ICE's first president. It can be awarded in gold ...
People acquainted with Thomas Telford
* Charles Atherton, fellow civil engineer * Hugh Baird (engineer), fellow civil engineer *Hamilton Fulton
Hamilton Fulton (26 May 1781 – 30 October 1833) was a Scottish civil engineer who worked for John Rennie and Thomas Telford before moving for a decade to the state of North Carolina as its principal engineer. Thereafter, he returned to Britain. ...
, fellow civil engineer
* John Gibb (engineer)
John Gibb (1776–1850) was a Scottish civil engineer and contractor whose work included the construction of harbours, bridges, roads, lighthouses, and railways in the United Kingdom, primarily in Scotland. He was a close associate of Thomas Te ...
, fellow civil engineer
* William Hazledine
William Hazledine (1763 – 26 October 1840) was an English ironmaster. Establishing large foundries, he was a pioneer in casting structural ironwork, most notably for canal aqueducts and early suspension bridges. Many of these projects were c ...
, supplied ironwork for many projects of Thomas Telford
* William Jessop
William Jessop (23 January 1745 – 18 November 1814) was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Early life
Jessop was born in Devonport, Devon, the ...
, fellow civil engineer
* John Benjamin Macneill
Sir John Benjamin Macneill FRS (1793 – 2 March 1880) was an eminent Irish civil engineer of the 19th century, closely associated with Thomas Telford. His most notable projects were railway schemes in Ireland.
Life
He was born in Mountpleasant ...
, fellow civil engineer
* Sir William Pulteney, 5th Baronet
Sir William Pulteney, 5th Baronet (October 1729 – 30 May 1805), known as William Johnstone until 1767, was a Scottish advocate, landowner and politician who sat in the House of Commons between 1768 and 1805. He was reputedly the wealthiest ...
, patron of Thomas Telford
* William Reynolds (industrialist)
William Reynolds (14 April 1758 – 3 June 1803) was an ironmaster and a partner in the ironworks in Coalbrookdale in Shropshire, England. He was interested in advances in science and industry, and invented the inclined plane for canals.
Early li ...
, constructed Longdon-on-Tern Aqueduct
The Longdon-on-Tern Aqueduct, near Longdon-on-Tern in Shropshire, was one of the first two canal aqueducts to be built from cast iron.
History
The cast iron canal aqueduct was re-engineered by Thomas Telford after the first construction desig ...
for Telford
* George Turnbull (civil engineer)
George Turnbull was a British engineer responsible from 1851 to 1863 for construction of the first railway line from Calcutta to Benares, some – later extended to Delhi. Turnbull was acclaimed by the Indian government as the "first railway ...
, fellow civil engineer
Notes
References
External links
Menai Heritage
A community project and museum telling the story of Thomas Telford's Menai Suspension bridge
Revolutionary Players website
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Telford, Thomas 1757 births 1834 deaths British bridge engineers Scottish architects Scottish civil engineers Scottish philanthropists Scottish stonemasons Scottish autobiographers Fellows of the Royal Society Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Members of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences People from Dumfries and Galloway People of the Industrial Revolution Burials at Westminster Abbey British canal engineers Presidents of the Institution of Civil Engineers Harbour engineers Scottish Engineering Hall of Fame inductees